Disclosure: I am compensated for purchases made through some links on this site. Click for details.
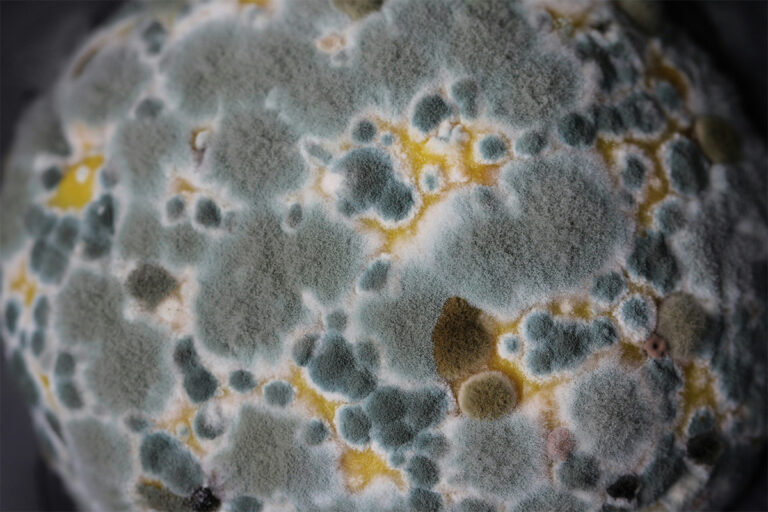
Green mold is a collective term for several species of fungi that predominantly have green spores, although their coloring can range from blue to pink in some situations. These molds are commonly found in both outdoor and indoor environments, especially in areas where moisture levels are high. The presence of green mold can influence indoor air quality and may be a concern if it appears on various surfaces in homes or buildings.
These molds, including species such as Cladosporium, Aspergillus, and Penicillium, are not all inherently dangerous, but some can be associated with health problems in sensitive individuals. The spores, which are a natural part of the mold’s reproductive cycle, can be an allergen and are of particular concern in indoor environments. Continuous exposure to mold spores can lead to respiratory issues or exacerbate existing health conditions.
Addressing green mold typically involves assessing the extent of the infestation, identifying the underlying cause of moisture buildup, and undertaking the necessary steps to remove the mold safely and prevent its return. Professional remediation may be required for large outbreaks or when the mold is found in HVAC systems to ensure that removal is thorough and effective.
Key Takeaways
- Green mold refers to various fungi known for green spores, impacting indoor air quality.
- Exposure to mold spores can lead to health problems, particularly in sensitive individuals.
- Effective mold remediation includes moisture control and may require professional intervention.
Understanding Green Mold
Green mold is a term for various fungi species, including Aspergillus, Cladosporium, and Penicillium, which are prevalent in environments with moisture and organic materials. These species can become problematic in indoor spaces, leading to health issues, especially in individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
Types and Identification
Aspergillus, Cladosporium, and Penicillium represent the primary genera of green mold, with the potential to exhibit a range of colors beyond green. Identifying mold typically involves assessing the color and texture of the spores, which can appear cottony or velvety. Visible mold growth on surfaces such as wood and drywall can indicate an underlying moisture problem.
Causes and Common Locations
Moisture and organic material are the key drivers of mold growth, and common locations include basements, bathrooms, and areas with high humidity and indoor dampness. Poor ventilation can lead to increased moisture accumulation, making spots near leaky windows or humid areas prime for green mold development.
Health Implications of Exposure
Exposure to green mold spores can cause a variety of health problems, such as respiratory issues, skin irritation, and allergic reactions. People with asthma or a compromised immune system may be at higher risk for serious complications like pneumonia or infections when exposed to mold and its mycotoxins.
Differences from Other Molds
Green mold differs from types like black mold (Stachybotrys chartarum) in color and toxicity; black mold is often associated with potent toxins. However, all molds can cause allergic reactions and should be addressed promptly to minimize health risks.
Prevention Tips
Controlling humidity is essential for mold prevention. Use humidifiers, ensure proper ventilation, especially in bathrooms and kitchens, and consider mold-resistant paints for areas prone to dampness. Regularly inspect potential problem areas to catch early signs of mold growth.
DIY Mold Removal Strategies
For minor mold issues, DIY mold removal can be effective using natural solutions like vinegar or a bleach solution. Always wear protective gear such as gloves and masks when cleaning mold. For larger infestations, it is recommended to seek professional help to clean up mold safely.
Professional Mold Remediation
Professional mold remediation involves a series of actions aimed at safely removing mold and preventing its future growth in a building. Employing an experienced team ensures that advanced techniques are used for a thorough and safe mold removal process.
When to Call a Professional
One should call a professional mold removal service when mold covers a significant area or is located in hard-to-reach places. It is especially crucial to seek professional help if occupants are experiencing health issues that may be related to mold exposure. These professionals use advanced testing methods to detect the presence and type of mold, ensuring accurate and reliable service.
The Mold Remediation Process
The mold remediation process generally begins with a thorough inspection and testing to identify the mold type and the affected areas. Remediation technicians then seal off the area to prevent the spread, use safety equipment to protect themselves, and implement strategies to safely remove the mold. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) vacuums and commercial-grade dehumidifiers are often used to remove spores and control humidity.
Related Content: How to Prepare for Mold Remediation: Steps for a Safe Process
Choosing a Mold Removal Service
Selecting a mold removal professional requires verifying their credentials, experience, and methods for ensuring air quality control. It is important to choose a service that utilizes proper safety equipment and follows guidelines for professional mold remediation. Look for businesses with good reviews that offer peace of mind through reliable and safe mold removal.
Post-Remediation Care
After remediation, regular inspection and maintenance are essential to prevent recurrence. Proper ventilation, use of dehumidifiers, and controlling indoor humidity levels are key to sustaining a mold-free environment. Regular maintenance checks and quick responses to water damage also play crucial roles in prevention.
Legal and Insurance Considerations
When dealing with mold, legal aspects may need to be addressed, particularly if health or property value is compromised. It’s important to understand the coverage terms of one’s insurance policy regarding mold damage. Professional remediation can also assist in documenting the process for potential insurance claims or compensation.
Health and Safety Measures
When dealing with green mold, one must understand the potential health risks and implement safety measures to mitigate those risks. Proper identification, cleaning methods, and strategies to improve air quality are essential in maintaining a healthy environment.
Recognizing Mold-Related Symptoms
Individuals who are exposed to mold can experience a range of health problems, especially respiratory issues. Common symptoms include sneezing, coughing, and skin rash. Some may suffer more severe reactions, such as asthma attacks or allergic responses like hay fever-type symptoms.
Treatment and Medical Advice
Treatment for mold exposure should be guided by healthcare professionals. Medications may alleviate allergy symptoms, but more severe mold-related conditions like aspergillosis require medical consultation. It’s imperative to seek professional advice if symptoms persist or worsen after exposure to mold spores.
Safe Cleaning Practices
Cleaning up mold involves safety protocols to prevent inhalation or contact with mold spores. Use protective gear like masks and gloves, and opt for non-toxic cleaners when possible. For significant mold infestations, professional remediation may be the safest approach to prevent health risks.
Related Content:
- Does Chlorine Dioxide Kill Mold: Efficacy and Use Cases Explained
- UV Light for Mold: Effective Sterilization Techniques
Improving Indoor Air Quality
Maintaining good indoor air quality is crucial in preventing the growth of mold and protecting health. Use a dehumidifier to control moisture, ensure proper ventilation in areas prone to dampness, and consider using air purifiers to reduce airborne mold spores. Regular maintenance of HVAC systems also helps in preventing the circulation of contaminants.
Case Studies and Research
Investigating green mold encompasses a spectrum of studies, ranging from the historical impact of mold infestations on properties and health to cutting-edge methods for detection and remediation. Here, research shines a light on the critical developments and ongoing inquiries into this pervasive issue.
Historical Cases of Mold Infestation
In the past, major mold cases have served as harbingers for an improved understanding of the health risks and property damage associated with mold. Notable infestations have led to refurbishment and better mold testing protocols. These historical events highlight the destructive potential of mold and underscore the necessity for vigilant detection and control.
Advancements in Mold Detection and Removal
Recent advancements in mold detection and removal apply novel methods and advanced techniques, utilizing state-of-the-art equipment. Researchers focus on creating more accurate mold detection technology, which offers the promise of faster response times and more efficient remediation efforts, minimizing the impact on both health and property.
Environmental Impact of Mold
Environmental studies have documented the occurrence of mold outdoors, exploring its role within the ecosystem. These studies examine how environmental mold growth can influence property damage and the broader environment. Ongoing research aims to mitigate the long-term impact of mold, with a focus on sustaining a balanced ecological presence.
Ongoing Studies in Mold-Related Health Effects
Medical research continues to probe the health effects of mold exposure. Numerous public health studies have attempted to understand the connection between mold and health problems, establishing a critical basis for current and future interventions. These ongoing studies are vital for devising strategies to protect individuals from the negative health consequences associated with mold exposure.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing green mold is essential for maintaining a healthy living environment.
Green mold, represented by species such as Aspergillus, Cladosporium, and Penicillium, thrives in moist conditions and can pose various health risks, especially to individuals with respiratory sensitivities or weakened immune systems.
Recognizing the causes and common locations of mold growth enables effective prevention and mitigation strategies. While minor infestations may be managed with DIY methods, significant outbreaks necessitate professional remediation to ensure thorough removal and prevent future growth.
By implementing preventative measures, such as controlling indoor humidity and ensuring proper ventilation, homeowners can significantly reduce the risk of mold proliferation. Regular maintenance and vigilance are key to protecting your health and property from the potential dangers of green mold.